Sustainable Development: A Clear Definition and Why It Matters
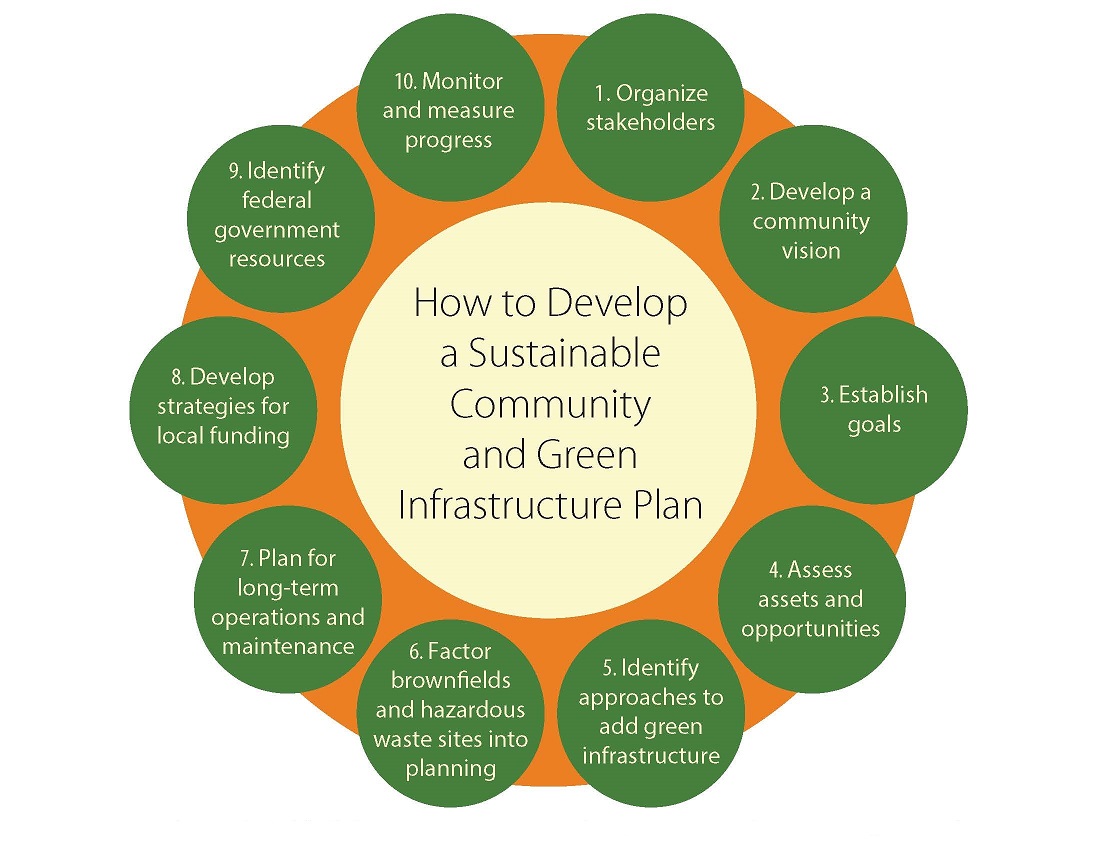
In today's world, the term sustainable development frequently surfaces in discussions concerning global health, environmental policy, and economic strategies. But what does this phrase mean, and why does it hold such importance in modern society?
What is Sustainable Development?
Sustainable development refers to the development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. This concept involves three fundamental pillars:
- Environmental sustainability: Protecting natural resources and ecosystems.
- Economic sustainability: Ensuring economic growth does not deplete natural or human capital.
- Social sustainability: Promoting social inclusion, equity, and justice.

Why Sustainable Development Matters
The significance of sustainable development can be broken down into several key reasons:
1. Preservation of Natural Resources
Natural resources like water, air, forests, and minerals are critical for human survival and quality of life. Sustainable practices ensure these resources are used in a way that they can regenerate or be replenished over time.
2. Climate Change Mitigation
Addressing climate change is perhaps one of the most pressing reasons for sustainable development. Sustainable practices reduce greenhouse gas emissions, aiming to limit global warming to below 2 degrees Celsius, as per international agreements like the Paris Accord.
3. Economic Benefits
Economies that prioritize sustainability often experience several benefits:
- Increased innovation due to the need for sustainable technologies.
- Long-term cost savings from energy efficiency and waste reduction.
- Job creation in green sectors like renewable energy, sustainable agriculture, and eco-tourism.
4. Social Equity and Inclusion
Sustainable development seeks to level the playing field, ensuring that development benefits are accessible to all segments of society, reducing disparities in wealth and opportunity.
5. Health and Well-being
Cleaner environments lead to better health outcomes, reducing the burden of diseases caused by pollution and poor living conditions.
Implementing Sustainable Development
To put sustainable development into practice, various steps can be taken:
Legislation and Policy
- Government regulations that enforce sustainability in industries.
- Tax incentives or subsidies for environmentally friendly practices.
Community Engagement
- Education and awareness campaigns to foster community involvement.
- Participatory decision-making processes that include local stakeholders.
Corporate Responsibility
- Integration of Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) criteria into business operations.
- Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) initiatives aimed at environmental conservation and community upliftment.
💡 Note: Sustainable development requires a collective effort, where every sector from governments to individuals plays a role.
Case Studies of Sustainable Development
Costa Rica
Costa Rica has become a global leader in sustainable development, with policies aimed at achieving carbon neutrality, promoting renewable energy, and preserving biodiversity. Their efforts have included:
- Payment for Ecosystem Services (PES), where landowners are compensated for maintaining forests.
- Over 98% of its electricity comes from renewable sources, mostly hydroelectric and geothermal.
Sweden
Sweden aims to be fossil-fuel-free by 2045. Key initiatives include:
- Urban planning with green spaces and bike-friendly infrastructure.
- Investment in bioenergy, wind, solar, and other renewables to replace traditional energy sources.
🍃 Note: Learning from global examples can provide insights into what might work in different contexts.
Challenges in Implementing Sustainable Development
The journey towards sustainability is not without its hurdles:
Economic Trade-offs
There can be initial economic costs associated with transitioning to sustainable practices, which might deter short-term profits.
Political Will
Sustainable development often requires long-term planning and policies, which might not align with political cycles that seek short-term gains.
Technological Innovation
The development and adoption of new technologies for sustainability can be slow, expensive, or unavailable in some regions.
Final Thoughts on Sustainable Development
As we navigate through the 21st century, the path towards sustainable development has become not just a choice but a necessity. The importance of sustainable development is rooted in the need to balance our current lifestyles with the needs of future generations. It promotes a holistic approach to growth, combining environmental care, economic viability, and social justice. By understanding and implementing the principles of sustainable development, we can work towards a world where progress does not come at the expense of the planet or its inhabitants.
What are the main goals of sustainable development?
+The primary goals of sustainable development include:
- Preserving the environment for future generations.
- Eradicating poverty and hunger.
- Promoting health and well-being.
- Ensuring access to clean water and sanitation.
- Reducing inequalities within and among countries.
- Stimulating economic growth while promoting sustainability.
How can individuals contribute to sustainable development?
+Individuals can contribute by:
- Reducing their carbon footprint through less car usage, energy efficiency at home, and waste reduction.
- Supporting and buying from sustainable businesses.
- Advocating for sustainable policies and practices.
- Engaging in or supporting conservation efforts like planting trees or protecting local ecosystems.
Are there any global agreements on sustainable development?
+Yes, there are several key global agreements:
- The Rio Declaration: Established the principles for sustainable development at the Earth Summit in 1992.
- Agenda 21: An action plan of the United Nations for sustainable development.
- The United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs): A set of 17 goals to achieve by 2030.
- The Paris Agreement: Aiming to keep global warming below 2°C.
Related Terms:
- Pembangunan berkelanjutan
- Keberlanjutan
- Kesetaraan gender
- Lingkungan hidup
- Pendidikan
- Kesehatan



